What and where are the stack and heap?
Programming language books explain that value types are created on the stack, and reference types are created on the heap, without explaining what these two things are. I haven't read a clear explanation of this. I understand what a stack is. But,
The stack is the memory set aside as scratch space for a thread of execution. When a function is called, a block is reserved on the top of the stack for local variables and some bookkeeping data. When that function returns, the block becomes unused and can be used the next time a function is called. The stack is always reserved in a LIFO (last in first out) order; the most recently reserved block is always the next block to be freed. This makes it really simple to keep track of the stack; freeing a block from the stack is nothing more than adjusting one pointer.
The heap is memory set aside for dynamic allocation. Unlike the stack, there's no enforced pattern to the allocation and deallocation of blocks from the heap; you can allocate a block at any time and free it at any time. This makes it much more complex to keep track of which parts of the heap are allocated or free at any given time; there are many custom heap allocators available to tune heap performance for different usage patterns.
Each thread gets a stack, while there's typically only one heap for the application (although it isn't uncommon to have multiple heaps for different types of allocation).
To answer your questions directly:
To what extent are they controlled by the OS or language runtime?
The OS allocates the stack for each system-level thread when the thread is created. Typically the OS is called by the language runtime to allocate the heap for the application.
What is their scope?
The stack is attached to a thread, so when the thread exits the stack is reclaimed. The heap is typically allocated at application startup by the runtime, and is reclaimed when the application (technically process) exits.
What determines the size of each of them?
The size of the stack is set when a thread is created. The size of the heap is set on application startup, but can grow as space is needed (the allocator requests more memory from the operating system).
What makes one faster?
The stack is faster because the access pattern makes it trivial to allocate and deallocate memory from it (a pointer/integer is simply incremented or decremented), while the heap has much more complex bookkeeping involved in an allocation or deallocation. Also, each byte in the stack tends to be reused very frequently which means it tends to be mapped to the processor's cache, making it very fast. Another performance hit for the heap is that the heap, being mostly a global resource, typically has to be multi-threading safe, i.e. each allocation and deallocation needs to be - typically - synchronized with "all" other heap accesses in the program.
A clear demonstration:
Image source: vikashazrati.wordpress.com
Stack:
Heap:
Example:
The most important point is that heap and stack are generic terms for ways in which memory can be allocated. They can be implemented in many different ways, and the terms apply to the basic concepts.
In a stack of items, items sit one on top of the other in the order they were placed there, and you can only remove the top one (without toppling the whole thing over).

The simplicity of a stack is that you do not need to maintain a table containing a record of each section of allocated memory; the only state information you need is a single pointer to the end of the stack. To allocate and de-allocate, you just increment and decrement that single pointer. Note: a stack can sometimes be implemented to start at the top of a section of memory and extend downwards rather than growing upwards.
In a heap, there is no particular order to the way items are placed. You can reach in and remove items in any order because there is no clear 'top' item.

Heap allocation requires maintaining a full record of what memory is allocated and what isn't, as well as some overhead maintenance to reduce fragmentation, find contiguous memory segments big enough to fit the requested size, and so on. Memory can be deallocated at any time leaving free space. Sometimes a memory allocator will perform maintenance tasks such as defragmenting memory by moving allocated memory around, or garbage collecting - identifying at runtime when memory is no longer in scope and deallocating it.
These images should do a fairly good job of describing the two ways of allocating and freeing memory in a stack and a heap. Yum!
To what extent are they controlled by the OS or language runtime?
As mentioned, heap and stack are general terms, and can be implemented in many ways. Computer programs typically have a stack called a call stack which stores information relevant to the current function such as a pointer to whichever function it was called from, and any local variables. Because functions call other functions and then return, the stack grows and shrinks to hold information from the functions further down the call stack. A program doesn't really have runtime control over it; it's determined by the programming language, OS and even the system architecture.
A heap is a general term used for any memory that is allocated dynamically and randomly; i.e. out of order. The memory is typically allocated by the OS, with the application calling API functions to do this allocation. There is a fair bit of overhead required in managing dynamically allocated memory, which is usually handled by the OS.
What is their scope?
The call stack is such a low level concept that it doesn't relate to 'scope' in the sense of programming. If you disassemble some code you'll see relative pointer style references to portions of the stack, but as far as a higher level language is concerned, the language imposes its own rules of scope. One important aspect of a stack, however, is that once a function returns, anything local to that function is immediately freed from the stack. That works the way you'd expect it to work given how your programming languages work. In a heap, it's also difficult to define. The scope is whatever is exposed by the OS, but your programming language probably adds its rules about what a "scope" is in your application. The processor architecture and the OS use virtual addressing, which the processor translates to physical addresses and there are page faults, etc. They keep track of what pages belong to which applications. You never really need to worry about this, though, because you just use whatever method your programming language uses to allocate and free memory, and check for errors (if the allocation/freeing fails for any reason).
What determines the size of each of them?
Again, it depends on the language, compiler, operating system and architecture. A stack is usually pre-allocated, because by definition it must be contiguous memory (more on that in the last paragraph). The language compiler or the OS determine its size. You don't store huge chunks of data on the stack, so it'll be big enough that it should never be fully used, except in cases of unwanted endless recursion (hence, "stack overflow") or other unusual programming decisions.
A heap is a general term for anything that can be dynamically allocated. Depending on which way you look at it, it is constantly changing size. In modern processors and operating systems the exact way it works is very abstracted anyway, so you don't normally need to worry much about how it works deep down, except that (in languages where it lets you) you mustn't use memory that you haven't allocated yet or memory that you have freed.
What makes one faster?
The stack is faster because all free memory is always contiguous. No list needs to be maintained of all the segments of free memory, just a single pointer to the current top of the stack. Compilers usually store this pointer in a special, fast register for this purpose. What's more, subsequent operations on a stack are usually concentrated within very nearby areas of memory, which at a very low level is good for optimization by the processor on-die caches.
(I have moved this answer from another question that was more or less a dupe of this one.)
The answer to your question is implementation specific and may vary across compilers and processor architectures. However, here is a simplified explanation.


Can a function be allocated on the heap instead of a stack?
No, activation records for functions (i.e. local or automatic variables) are allocated on the stack that is used not only to store these variables, but also to keep track of nested function calls.
How the heap is managed is really up to the runtime environment. C uses malloc and C++ uses new, but many other languages have garbage collection.
However, the stack is a more low-level feature closely tied to the processor architecture. Growing the heap when there is not enough space isn't too hard since it can be implemented in the library call that handles the heap. However, growing the stack is often impossible as the stack overflow only is discovered when it is too late; and shutting down the thread of execution is the only viable option.
In the following C# code
Here's how the memory is managed

Local Variables that only need to last as long as the function invocation go in the stack. The heap is used for variables whose lifetime we don't really know up front but we expect them to last a while. In most languages it's critical that we know at compile time how large a variable is if we want to store it on the stack.
Objects (which vary in size as we update them) go on the heap because we don't know at creation time how long they are going to last. In many languages the heap is garbage collected to find objects (such as the cls1 object) that no longer have any references.
In Java, most objects go directly into the heap. In languages like C / C++, structs and classes can often remain on the stack when you're not dealing with pointers.
More information can be found here:
The difference between stack and heap memory allocation « timmurphy.org
and here:
Creating Objects on the Stack and Heap
This article is the source of picture above: Six important .NET concepts: Stack, heap, value types, reference types, boxing, and unboxing - CodeProject
but be aware it may contain some inaccuracies.
The Stack
When you call a function the arguments to that function plus some other overhead is put on the stack. Some info (such as where to go on return) is also stored there.
When you declare a variable inside your function, that variable is also allocated on the stack.
Deallocating the stack is pretty simple because you always deallocate in the reverse order in which you allocate. Stack stuff is added as you enter functions, the corresponding data is removed as you exit them. This means that you tend to stay within a small region of the stack unless you call lots of functions that call lots of other functions (or create a recursive solution).
The Heap
The heap is a generic name for where you put the data that you create on the fly. If you don't know how many spaceships your program is going to create, you are likely to use the new (or malloc or equivalent) operator to create each spaceship. This allocation is going to stick around for a while, so it is likely we will free things in a different order than we created them.
Thus, the heap is far more complex, because there end up being regions of memory that are unused interleaved with chunks that are - memory gets fragmented. Finding free memory of the size you need is a difficult problem. This is why the heap should be avoided (though it is still often used).
Implementation
Implementation of both the stack and heap is usually down to the runtime / OS. Often games and other applications that are performance critical create their own memory solutions that grab a large chunk of memory from the heap and then dish it out internally to avoid relying on the OS for memory.
This is only practical if your memory usage is quite different from the norm - i.e for games where you load a level in one huge operation and can chuck the whole lot away in another huge operation.
Physical location in memory
This is less relevant than you think because of a technology called Virtual Memory which makes your program think that you have access to a certain address where the physical data is somewhere else (even on the hard disc!). The addresses you get for the stack are in increasing order as your call tree gets deeper. The addresses for the heap are un-predictable (i.e implimentation specific) and frankly not important.
To clarify, this answer has incorrect information (thomas fixed his answer after comments, cool :) ). Other answers just avoid explaining what static allocation means. So I will explain the three main forms of allocation and how they usually relate to the heap, stack, and data segment below. I also will show some examples in both C/C++ and Python to help people understand.
"Static" (AKA statically allocated) variables are not allocated on the stack. Do not assume so - many people do only because "static" sounds a lot like "stack". They actually exist in neither the stack nor the heap. The are part of what's called the data segment.
However, it is generally better to consider "scope" and "lifetime" rather than "stack" and "heap".
Scope refers to what parts of the code can access a variable. Generally we think of local scope (can only be accessed by the current function) versus global scope (can be accessed anywhere) although scope can get much more complex.
Lifetime refers to when a variable is allocated and deallocated during program execution. Usually we think of static allocation (variable will persist through the entire duration of the program, making it useful for storing the same information across several function calls) versus automatic allocation (variable only persists during a single call to a function, making it useful for storing information that is only used during your function and can be discarded once you are done) versus dynamic allocation (variables whose duration is defined at runtime, instead of compile time like static or automatic).
Although most compilers and interpreters implement this behavior similarly in terms of using stacks, heaps, etc, a compiler may sometimes break these conventions if it wants as long as behavior is correct. For instance, due to optimization a local variable may only exist in a register or be removed entirely, even though most local variables exist in the stack. As has been pointed out in a few comments, you are free to implement a compiler that doesn't even use a stack or a heap, but instead some other storage mechanisms (rarely done, since stacks and heaps are great for this).
I will provide some simple annotated C code to illustrate all of this. The best way to learn is to run a program under a debugger and watch the behavior. If you prefer to read python, skip to the end of the answer :)
A particularly poignant example of why it's important to distinguish between lifetime and scope is that a variable can have local scope but static lifetime - for instance, "someLocalStaticVariable" in the code sample above. Such variables can make our common but informal naming habits very confusing. For instance when we say "local" we usually mean "locally scoped automatically allocated variable" and when we say global we usually mean "globally scoped statically allocated variable". Unfortunately when it comes to things like "file scoped statically allocated variables" many people just say... "huh???".
Some of the syntax choices in C/C++ exacerbate this problem - for instance many people think global variables are not "static" because of the syntax shown below.
Note that putting the keyword "static" in the declaration above prevents var2 from having global scope. Nevertheless, the global var1 has static allocation. This is not intuitive! For this reason, I try to never use the word "static" when describing scope, and instead say something like "file" or "file limited" scope. However many people use the phrase "static" or "static scope" to describe a variable that can only be accessed from one code file. In the context of lifetime, "static" always means the variable is allocated at program start and deallocated when program exits.
Some people think of these concepts as C/C++ specific. They are not. For instance, the Python sample below illustrates all three types of allocation (there are some subtle differences possible in interpreted languages that I won't get into here).
Others have answered the broad strokes pretty well, so I'll throw in a few details.
Stack and heap need not be singular. A common situation in which you have more than one stack is if you have more than one thread in a process. In this case each thread has its own stack. You can also have more than one heap, for example some DLL configurations can result in different DLLs allocating from different heaps, which is why it's generally a bad idea to release memory allocated by a different library.
In C you can get the benefit of variable length allocation through the use of alloca, which allocates on the stack, as opposed to alloc, which allocates on the heap. This memory won't survive your return statement, but it's useful for a scratch buffer.
Making a huge temporary buffer on Windows that you don't use much of is not free. This is because the compiler will generate a stack probe loop that is called every time your function is entered to make sure the stack exists (because Windows uses a single guard page at the end of your stack to detect when it needs to grow the stack. If you access memory more than one page off the end of the stack you will crash). Example:
Others have directly answered your question, but when trying to understand the stack and the heap, I think it is helpful to consider the memory layout of a traditional UNIX process (without threads and mmap()-based allocators). The Memory Management Glossary web page has a diagram of this memory layout.
The stack and heap are traditionally located at opposite ends of the process's virtual address space. The stack grows automatically when accessed, up to a size set by the kernel (which can be adjusted with setrlimit(RLIMIT_STACK, ...)). The heap grows when the memory allocator invokes the brk() or sbrk() system call, mapping more pages of physical memory into the process's virtual address space.
In systems without virtual memory, such as some embedded systems, the same basic layout often applies, except the stack and heap are fixed in size. However, in other embedded systems (such as those based on Microchip PIC microcontrollers), the program stack is a separate block of memory that is not addressable by data movement instructions, and can only be modified or read indirectly through program flow instructions (call, return, etc.). Other architectures, such as Intel Itanium processors, have multiple stacks. In this sense, the stack is an element of the CPU architecture.
I think many other people have given you mostly correct answers on this matter.
One detail that has been missed, however, is that the "heap" should in fact probably be called the "free store". The reason for this distinction is that the original free store was implemented with a data structure known as a "binomial heap." For that reason, allocating from early implementations of malloc()/free() was allocation from a heap. However, in this modern day, most free stores are implemented with very elaborate data structures that are not binomial heaps.
The stack is a portion of memory that can be manipulated via several key assembly language instructions, such as 'pop' (remove and return a value from the stack) and 'push' (push a value to the stack), but also call (call a subroutine - this pushes the address to return to the stack) and return (return from a subroutine - this pops the address off of the stack and jumps to it). It's the region of memory below the stack pointer register, which can be set as needed. The stack is also used for passing arguments to subroutines, and also for preserving the values in registers before calling subroutines.
The heap is a portion of memory that is given to an application by the operating system, typically through a syscall like malloc. On modern OSes this memory is a set of pages that only the calling process has access to.
The size of the stack is determined at runtime, and generally does not grow after the program launches. In a C program, the stack needs to be large enough to hold every variable declared within each function. The heap will grow dynamically as needed, but the OS is ultimately making the call (it will often grow the heap by more than the value requested by malloc, so that at least some future mallocs won't need to go back to the kernel to get more memory. This behavior is often customizable)
Because you've allocated the stack before launching the program, you never need to malloc before you can use the stack, so that's a slight advantage there. In practice, it's very hard to predict what will be fast and what will be slow in modern operating systems that have virtual memory subsystems, because how the pages are implemented and where they are stored is an implementation detail.
What is a stack?
A stack is a pile of objects, typically one that is neatly arranged.

Stacks in computing architectures are regions of memory where data is added or removed in a last-in-first-out manner.
In a multi-threaded application, each thread will have its own stack.
What is a heap?
A heap is an untidy collection of things piled up haphazardly.

In computing architectures the heap is an area of dynamically-allocated memory that is managed automatically by the operating system or the memory manager library.
Memory on the heap is allocated, deallocated, and resized regularly during program execution, and this can lead to a problem called fragmentation.
Fragmentation occurs when memory objects are allocated with small spaces in between that are too small to hold additional memory objects.
The net result is a percentage of the heap space that is not usable for further memory allocations.
Both together
In a multi-threaded application, each thread will have its own stack. But, all the different threads will share the heap.
Because the different threads share the heap in a multi-threaded application, this also means that there has to be some coordination between the threads so that they don’t try to access and manipulate the same piece(s) of memory in the heap at the same time.
Which is faster – the stack or the heap? And why?
The stack is much faster than the heap.
This is because of the way that memory is allocated on the stack.
Allocating memory on the stack is as simple as moving the stack pointer up.
For people new to programming, it’s probably a good idea to use the stack since it’s easier.
Because the stack is small, you would want to use it when you know exactly how much memory you will need for your data, or if you know the size of your data is very small.
It’s better to use the heap when you know that you will need a lot of memory for your data, or you just are not sure how much memory you will need (like with a dynamic array).

The stack is the area of memory where local variables (including method parameters) are stored. When it comes to object variables, these are merely references (pointers) to the actual objects on the heap.
Every time an object is instantiated, a chunk of heap memory is set aside to hold the data (state) of that object. Since objects can contain other objects, some of this data can in fact hold references to those nested objects.
You can do some interesting things with the stack. For instance, you have functions like alloca (assuming you can get past the copious warnings concerning its use), which is a form of malloc that specifically uses the stack, not the heap, for memory.
That said, stack-based memory errors are some of the worst I've experienced. If you use heap memory, and you overstep the bounds of your allocated block, you have a decent chance of triggering a segment fault. (Not 100%: your block may be incidentally contiguous with another that you have previously allocated.) But since variables created on the stack are always contiguous with each other, writing out of bounds can change the value of another variable. I have learned that whenever I feel that my program has stopped obeying the laws of logic, it is probably buffer overflow.
Simply, the stack is where local variables get created. Also, every time you call a subroutine the program counter (pointer to the next machine instruction) and any important registers, and sometimes the parameters get pushed on the stack. Then any local variables inside the subroutine are pushed onto the stack (and used from there). When the subroutine finishes, that stuff all gets popped back off the stack. The PC and register data gets and put back where it was as it is popped, so your program can go on its merry way.
The heap is the area of memory dynamic memory allocations are made out of (explicit "new" or "allocate" calls). It is a special data structure that can keep track of blocks of memory of varying sizes and their allocation status.
In "classic" systems RAM was laid out such that the stack pointer started out at the bottom of memory, the heap pointer started out at the top, and they grew towards each other. If they overlap, you are out of RAM. That doesn't work with modern multi-threaded OSes though. Every thread has to have its own stack, and those can get created dynamicly.
From WikiAnwser.
When a function or a method calls another function which in turns calls another function, etc., the execution of all those functions remains suspended until the very last function returns its value.
This chain of suspended function calls is the stack, because elements in the stack (function calls) depend on each other.
The stack is important to consider in exception handling and thread executions.
The heap is simply the memory used by programs to store variables.
Element of the heap (variables) have no dependencies with each other and can always be accessed randomly at any time.
Stack
Heap
In the 1980s, UNIX propagated like bunnies with big companies rolling their own.
Exxon had one as did dozens of brand names lost to history.
How memory was laid out was at the discretion of the many implementors.
A typical C program was laid out flat in memory with
an opportunity to increase by changing the brk() value.
Typically, the HEAP was just below this brk value
and increasing brk increased the amount of available heap.
The single STACK was typically an area below HEAP which was a tract of memory
containing nothing of value until the top of the next fixed block of memory.
This next block was often CODE which could be overwritten by stack data
in one of the famous hacks of its era.
One typical memory block was BSS (a block of zero values)
which was accidentally not zeroed in one manufacturer's offering.
Another was DATA containing initialized values, including strings and numbers.
A third was CODE containing CRT (C runtime), main, functions, and libraries.
The advent of virtual memory in UNIX changes many of the constraints.
There is no objective reason why these blocks need be contiguous,
or fixed in size, or ordered a particular way now.
Of course, before UNIX was Multics which didn't suffer from these constraints.
Here is a schematic showing one of the memory layouts of that era.

Physical memory is the range of the physical addresses of the memory cells in which an application or system stores its data, code, and so on during execution. Memory management denotes the managing of these physical addresses by swapping the data from physical memory to a storage device and then back to physical memory when needed. The OS implements the memory management services using virtual memory. As a C# application developer you do not need to write any memory management services. The CLR uses the underlying OS memory management services to provide the memory model for C# or any other high-level language targeting the CLR.
Figure 4-1 shows physical memory that has been abstracted and managed by the OS, using the virtual memory concept. Virtual memory is the abstract view of the physical memory, managed by the OS. Virtual memory is simply a series of virtual addresses, and these virtual addresses are translated by the CPU into the physical address when needed.
Figure 4-1. CLR memory abstraction

The CLR provides the memory management abstract layer for the virtual execution environment, using the operating memory services. The abstracted concepts the CLR uses are AppDomain, thread, stack, heapmemorymapped file, and so on. The concept of the application domain (AppDomain) gives your application an isolated execution environment.
By looking at the stack trace while debugging the following C# application, using WinDbg, you will see how the CLR uses the underlying OS memory management services (e.g., the HeapFree method from KERNEL32.dll, the RtlpFreeHeap method from ntdll.dll) to implement its own memory model:
The compiled assembly of the program is loaded into WinDbg to start debugging. You use the following
commands to initialize the debugging session:
0:000> sxe ld clrjit
0:000> g
0:000> .loadby sos clr
0:000> .load C:WindowsMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv4.0.30319sos.dll
Then, you set a breakpoint at the Main method of the Program class,
using the !bpmd command:
0:000>!bpmd CH_04.exe CH_04.Program.Main
To continue the execution and break at the breakpoint, execute the g
command:
0:000> g
When the execution breaks at the breakpoint, you use the !eestack command to view the stack trace details of all threads running for the current process. The following output shows the stack trace for all the threads running for the application CH_04.exe:
0:000> !eestack
Thread 0
Current frame: (MethodDesc 00233800 +0
CH_04.Program.Main(System.String))
ChildEBP RetAddr Caller, Callee
0022ed24 5faf21db clr!CallDescrWorker+0x33
/trace removed/
0022f218 77712d68 ntdll!RtlFreeHeap+0x142, calling ntdll!RtlpFreeHeap
0022f238 771df1ac KERNEL32!HeapFree+0x14, calling ntdll!RtlFreeHeap
0022f24c 5fb4c036 clr!EEHeapFree+0x36, calling KERNEL32!HeapFree
0022f260 5fb4c09d clr!EEHeapFreeInProcessHeap+0x24, calling
clr!EEHeapFree
0022f274 5fb4c06d clr!operator delete+0x30, calling
clr!EEHeapFreeInProcessHeap /trace removed/
0022f4d0 7771316f ntdll!RtlpFreeHeap+0xb7a, calling ntdll!_SEH_epilog4
0022f4d4 77712d68 ntdll!RtlFreeHeap+0x142, calling ntdll!RtlpFreeHeap
0022f4f4 771df1ac KERNEL32!HeapFree+0x14, calling ntdll!RtlFreeHeap
/trace removed/
This stack trace indicates that the CLR uses OS memory management services to implement its own memory model. Any memory operation in.NET goes via the CLR memory layer to the OS memory management layer.
Figure 4-2 illustrates a typical C# application memory model used by the CLR at runtime.
Figure 4-2. A typical C# application memory model
The CLR memory model is tightly coupled with the OS memory management services. To understand the CLR memory model, it is important to understand the underlying OS memory model. It is also crucial to know how the physical memory address space is abstracted into the virtual memory address space, the ways the virtual address space is being used by the user application and system application, how virtual-to-physical address mapping works, how memory-mapped file works, and so on. This background knowledge will improve your grasp of CLR memory model concepts, including AppDomain, stack, and heap.
For more information, refer to this book:
C# Deconstructed: Discover how C# works on the .NET Framework
This book + ClrViaC# + Windows Internals are excellent resources to known .net framework in depth and relation with OS.
A stack is used for static memory allocation and a heap for dynamic memory allocation, both stored in the computer's RAM.
The Stack
The stack is a "LIFO" (last in, first out) data structure, that is managed and optimized by the CPU quite closely. Every time a function declares a new variable, it is "pushed" onto the stack. Then every time a function exits, all of the variables pushed onto the stack by that function, are freed (that is to say, they are deleted). Once a stack variable is freed, that region of memory becomes available for other stack variables.
The advantage of using the stack to store variables, is that memory is managed for you. You don't have to allocate memory by hand, or free it once you don't need it any more. What's more, because the CPU organizes stack memory so efficiently, reading from and writing to stack variables is very fast.
More can be found here.
The Heap
The heap is a region of your computer's memory that is not managed automatically for you, and is not as tightly managed by the CPU. It is a more free-floating region of memory (and is larger). To allocate memory on the heap, you must use malloc() or calloc(), which are built-in C functions. Once you have allocated memory on the heap, you are responsible for using free() to deallocate that memory once you don't need it any more.
If you fail to do this, your program will have what is known as a memory leak. That is, memory on the heap will still be set aside (and won't be available to other processes). As we will see in the debugging section, there is a tool called Valgrind that can help you detect memory leaks.
Unlike the stack, the heap does not have size restrictions on variable size (apart from the obvious physical limitations of your computer). Heap memory is slightly slower to be read from and written to, because one has to use pointers to access memory on the heap. We will talk about pointers shortly.
Unlike the stack, variables created on the heap are accessible by any function, anywhere in your program. Heap variables are essentially global in scope.
More can be found here.
Variables allocated on the stack are stored directly to the memory and access to this memory is very fast, and its allocation is dealt with when the program is compiled. When a function or a method calls another function which in turns calls another function, etc., the execution of all those functions remains suspended until the very last function returns its value. The stack is always reserved in a LIFO order, the most recently reserved block is always the next block to be freed. This makes it really simple to keep track of the stack, freeing a block from the stack is nothing more than adjusting one pointer.
Variables allocated on the heap have their memory allocated at run time and accessing this memory is a bit slower, but the heap size is only limited by the size of virtual memory. Elements of the heap have no dependencies with each other and can always be accessed randomly at any time. You can allocate a block at any time and free it at any time. This makes it much more complex to keep track of which parts of the heap are allocated or free at any given time.

You can use the stack if you know exactly how much data you need to allocate before compile time, and it is not too big. You can use the heap if you don't know exactly how much data you will need at runtime or if you need to allocate a lot of data.
In a multi-threaded situation each thread will have its own completely independent stack, but they will share the heap. The stack is thread specific and the heap is application specific. The stack is important to consider in exception handling and thread executions.
Each thread gets a stack, while there's typically only one heap for the application (although it isn't uncommon to have multiple heaps for different types of allocation).

At run-time, if the application needs more heap, it can allocate memory from free memory and if the stack needs memory, it can allocate memory from free memory allocated memory for the application.
Even, more detail is given here and here.
Now come to your question's answers.
To what extent are they controlled by the OS or language runtime?
The OS allocates the stack for each system-level thread when the thread is created. Typically the OS is called by the language runtime to allocate the heap for the application.
More can be found here.
What is their scope?
Already given in top.
"You can use the stack if you know exactly how much data you need to allocate before compile time, and it is not too big. You can use the heap if you don't know exactly how much data you will need at runtime or if you need to allocate a lot of data."
More can be found in here.
What determines the size of each of them?
The size of the stack is set by OS when a thread is created. The size of the heap is set on application startup, but it can grow as space is needed (the allocator requests more memory from the operating system).
What makes one faster?
Stack allocation is much faster since all it really does is move the stack pointer. Using memory pools, you can get comparable performance out of heap allocation, but that comes with a slight added complexity and its own headaches.
Also, stack vs. heap is not only a performance consideration; it also tells you a lot about the expected lifetime of objects.
Details can be found from here.
A couple of cents: I think, it will be good to draw memory graphical and more simple:

Arrows - show where grow stack and heap, process stack size have limit, defined in OS, thread stack size limits by parameters in thread create API usually. Heap usually limiting by process maximum virtual memory size, for 32 bit 2-4 GB for example.
So simple way: process heap is general for process and all threads inside, using for memory allocation in common case with something like malloc().
Stack is quick memory for store in common case function return pointers and variables, processed as parameters in function call, local function variables.
Since some answers went nitpicking, I'm going to contribute my mite.
Surprisingly, no one has mentioned that multiple (i.e. not related to the number of running OS-level threads) call stacks are to be found not only in exotic languages (PostScript) or platforms (Intel Itanium), but also in fibers, green threads and some implementations of coroutines.
Fibers, green threads and coroutines are in many ways similar, which leads to much confusion. The difference between fibers and green threads is that the former use cooperative multitasking, while the latter may feature either cooperative or preemptive one (or even both). For the distinction between fibers and coroutines, see here.
In any case, the purpose of both fibers, green threads and coroutines is having multiple functions executing concurrently, but not in parallel (see this SO question for the distinction) within a single OS-level thread, transferring control back and forth from one another in an organized fashion.
When using fibers, green threads or coroutines, you usually have a separate stack per function. (Technically, not just a stack but a whole context of execution is per function. Most importantly, CPU registers.) For every thread there're as many stacks as there're concurrently running functions, and the thread is switching between executing each function according to the logic of your program. When a function runs to its end, its stack is destroyed. So, the number and lifetimes of stacks are dynamic and are not determined by the number of OS-level threads!
Note that I said "usually have a separate stack per function". There're both stackful and stackless implementations of couroutines. Most notable stackful C++ implementations are Boost.Coroutine and Microsoft PPL's async/await. (However, C++'s resumable functions (a.k.a. "async and await"), which were proposed to C++17, are likely to use stackless coroutines.)
Fibers proposal to the C++ standard library is forthcoming. Also, there're some third-party libraries. Green threads are extremely popular in languages like Python and Ruby.
OK, simply and in short words, they mean ordered and not ordered...!
Stack: In stack items, things get on the top of each-other, means gonna be faster and more efficient to be processed!...
So there is always an index to point the specific item, also processing gonna be faster, there is relationship between the items as well!...
Heap: No order, processing gonna be slower and values are messed up together with no specific order or index... there are random and there is no relationship between them... so execution and usage time could be vary...
I also create the image below to show how they may look like:

stack, heap and data of each process in virtual memory:
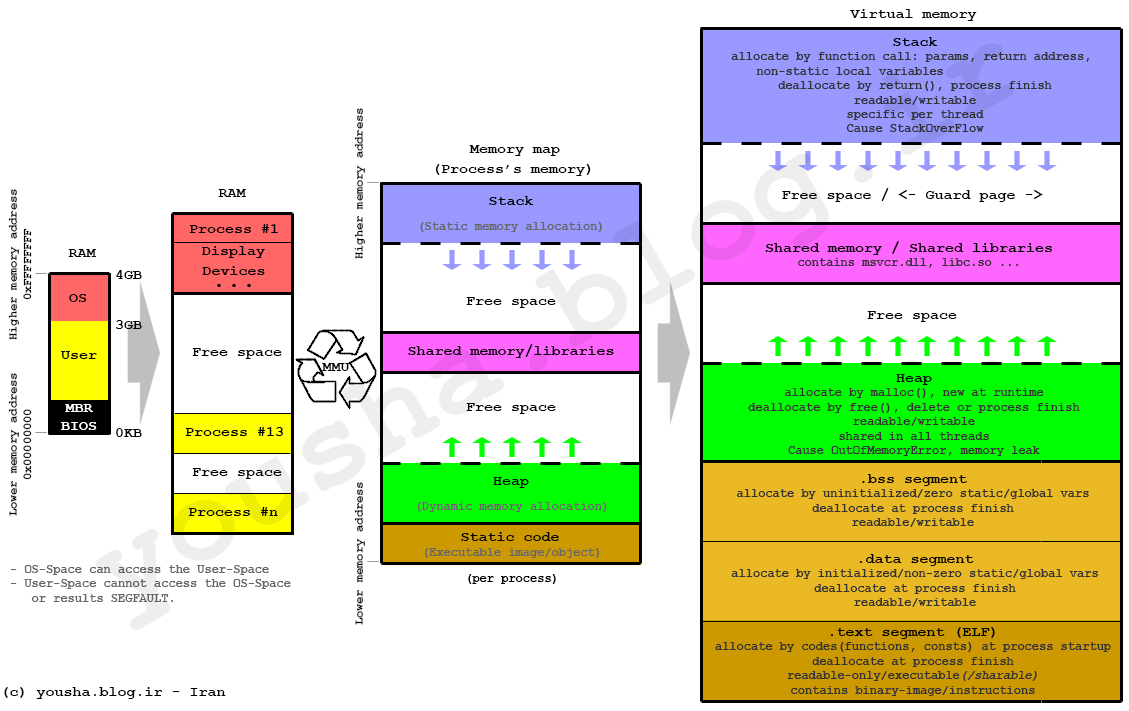
I have something to share with you, although major points are already penned.
Stack
Heap
Interesting note:
Feedbacks are wellcomed.
A lot of answers are correct as concepts, but we must note that a stack is needed by the hardware (i.e. microprocessor) to allow calling subroutines (CALL in assembly language..). (OOP guys will call it methods)
On the stack you save return addresses and call → push / ret → pop is managed directly in hardware.
You can use the stack to pass parameters.. even if it is slower than using registers (would a microprocessor guru say or a good 1980s BIOS book...)
Stack usage is faster as:
Thank you for your interest in this question.
Because it has attracted low-quality or spam answers that had to be removed, posting an answer now requires 10 reputation on this site (the association bonus does not count).
Would you like to answer one of these unanswered questions instead?
