Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Hohenzollern-Hechingen | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1576–1850 | |||||||||
 Flag  Coat of arms | |||||||||
Motto: Latin: Nihil Sine Deo (Nothing without God) | |||||||||
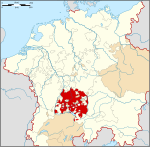
 Hohenzollern-Hechingen in 1848 | |||||||||
| Status | Principality | ||||||||
| Capital | Hechingen | ||||||||
| Common languages | Swabian German | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholic | ||||||||
| Government | Principality | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Partition of County of Hohenzollern | 1576 | ||||||||
• Raised to Principality | 1623 | ||||||||
• House extinction | 1869 | ||||||||
• Incorporation into Kingdom of Prussia | 1850 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Hohenzollern-Hechingen was a small principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to the Swabian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty.
Contents
1 History
2 Rulers
2.1 Counts of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1576–1623)[1]
2.2 Princes of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1623–1850)
3 References
4 External links
History[edit]

The New Castle at Hechingen
The County of Hohenzollern-Hechingen was created in 1576, upon the partition of the County of Hohenzollern, a fief of the Holy Roman Empire. When the last count of Hohenzollern, Charles I of Hohenzollern (1512–1579) died, the territory was to be divided up between his three sons:
Eitel Frederick IV of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1545–1605)
Charles II of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1547–1606)
Christopher of Hohenzollern-Haigerloch (1552–1592)
Unlike the Hohenzollerns of Brandenburg and Prussia, the Hohenzollerns of southwest Germany remained Roman Catholic. The County was raised to a principality in 1623.
The principality joined the Confederation of the Rhine in 1806 and was a member state of the German Confederation between 1815 and 1850. The democratic Revolution of 1848 was relatively successful in Hohenzollern, and on 16 May 1848, the Prince was forced to accept the establishment of a constitution. However, the conflict between monarch and democrats continued, and on 6 August, Hohenzollern was occupied by Prussian forces. On 7 December 1849, Prince Friedrich Wilhelm Konstantin sold the country to his relative, King Frederick William IV of Prussia. On 12 March 1850, Hohenzollern-Hechingen officially became part of Prussia, and formed together with Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen the Province of Hohenzollern.
Rulers[edit]

Arms of a Prince of Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Counts of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1576–1623)[1][edit]
.mw-parser-output .treeview ulpadding:0;margin:0.mw-parser-output .treeview lipadding:0;margin:0;list-style-type:none;list-style-image:none.mw-parser-output .treeview li libackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f2/Treeview-grey-line.png")no-repeat 0 -2981px;padding-left:21px;text-indent:0.3em.mw-parser-output .treeview li li:last-childbackground-position:0 -5971px.mw-parser-output .treeview li.emptyline>ul>.mw-empty-elt:first-child+.emptyline,.mw-parser-output .treeview li.emptyline>ul>li:first-childbackground-position:0 9px
Eitel Friedrich IV, Count 1576–1605 (1545-1605), eldest surviving son of Karl I of Hohenzollern
Johann Georg, Count 1605–1623 (1577-1623), created Reichsfürst von Hohenzollern-Hechingen 1623
Princes of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1623–1850)[edit]
Johann Georg, 1st Prince Mar 23-Sep 28 1623 (1577-1623)
Eitel Friedrich V, 2nd Prince 1623–1661 (1601-1661)
Philipp Christoph Friedrich, 3rd Prince 1661–1671 (1616-1671)
Friedrich Wilhelm, 4th Prince 1671–1735 (1663-1735)
Friedrich Ludwig, 5th Prince 1735–1750 (1688-1750)
Prince Hermann Friedrich of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1665-1733)
Josef Friedrich Wilhelm, 6th Prince 1750–1798 (1717-1798)
Prince Franz Xaver of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1720-1765)
Hermann, 7th Prince 1798–1810 (1751-1810)
Frederick, 8th Prince 1810–1838 (1776-1838)
Constantine, 9th Prince 1838–1850 (1801-1869), sons were without dynastic rights, the Counts of Rothenburg
- After cession of territory to Prussia, the Prince continued to use his title.
- Line became extinct 1869 at Prince Constantine's death, and titles passed to the Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen line.
References[edit]
^ Marek, Miroslav. "hohz/hohenz9.html". genealogy.euweb.cz. [self-published source][better source needed]
External links[edit]
- Almanach de Gotha info about Hohenzollern-Hechingen
Categories:
- 1850 disestablishments
- States and territories established in 1576
- Hechingen
- House of Hohenzollern-Hechingen
- States of the Confederation of the Rhine
- Principalities of the Holy Roman Empire
- States of the German Confederation
- Former states and territories of Baden-Württemberg
- Swabian Jura
- Early Modern history of Germany
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgPageParseReport":"limitreport":"cputime":"0.544","walltime":"0.730","ppvisitednodes":"value":3847,"limit":1000000,"ppgeneratednodes":"value":0,"limit":1500000,"postexpandincludesize":"value":113566,"limit":2097152,"templateargumentsize":"value":4622,"limit":2097152,"expansiondepth":"value":17,"limit":40,"expensivefunctioncount":"value":9,"limit":500,"unstrip-depth":"value":0,"limit":20,"unstrip-size":"value":2503,"limit":5000000,"entityaccesscount":"value":1,"limit":400,"timingprofile":["100.00% 600.300 1 -total"," 48.19% 289.289 1 Template:Infobox_Former_Country"," 41.85% 251.234 2 Template:Infobox"," 21.08% 126.534 1 Template:Lang-la"," 16.11% 96.713 1 Template:Reflist"," 10.94% 65.685 6 Template:Navbox"," 8.30% 49.841 1 Template:Authority_control"," 7.24% 43.487 2 Template:Fix"," 6.52% 39.165 1 Template:Refimprove"," 6.05% 36.301 1 Template:Self-published_source"],"scribunto":"limitreport-timeusage":"value":"0.257","limit":"10.000","limitreport-memusage":"value":13634723,"limit":52428800,"cachereport":"origin":"mw1274","timestamp":"20180831161325","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false);mw.config.set("wgBackendResponseTime":820,"wgHostname":"mw1274"););


 Clash Royale CLAN TAG
Clash Royale CLAN TAG