Lockyer (Martian crater)
Lockyer (Martian crater)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
 Topographic location of Lockyer Crater | |
| Planet | Mars |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 28°00′N 199°30′W / 28°N 199.5°W / 28; -199.5Coordinates: 28°00′N 199°30′W / 28°N 199.5°W / 28; -199.5 |
| Diameter | 71 km |
| Eponym | Joseph N. Lockyer, British astronomer (1836-1920). |
Lockyer is a crater in the Elysium quadrangle of Mars, located at 28° North and 199.5° West. It is 71 km in diameter and was named after Joseph N. Lockyer, a British astronomer (1836-1920).[1] Lockyer is fairly easy to spot on Mars maps because it sits in the relatively young northern hemisphere, where there are few craters. It is close to Elysium Mons and Hecates Tholus, two large volcanoes.
Phlegra Montes just north of the crater, a mountain range spanning over 1,350 km. Also there is one crater is located north-northeast, Adams.
Impact craters generally have a rim with ejecta around them, in contrast volcanic craters usually do not have a rim or ejecta deposits. As craters get larger (greater than 10 km in diameter) they usually have a central peak.[2] The peak is caused by a rebound of the crater floor following the impact.[3]

Lockyer, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Lockyer's central hills, as seen by HiRISE.

Layers in Lockyer, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program.
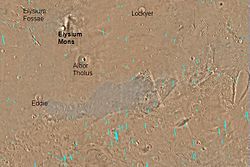
Map of Elysium quadrangle. Elysium Mons and Albor Tholus are large volcanoes. The crater Lockyer is at the top of the map.
See also[edit]
- Climate of Mars
- Geological history of Mars
- Geology of Mars
- Hesperian
- HiRISE
- HiWish program
- Impact crater
- Impact event
- List of craters on Mars
- Ore resources on Mars
- Planetary nomenclature
- Water on Mars
References[edit]
^ http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/
^ http://www.lpi.usra.edu/publications/slidesets/stones/
^ Hugh H. Kieffer (1992). Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
This article about the planet Mars or its moons is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This article about an extraterrestrial geological feature is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Categories:
- Elysium quadrangle
- Impact craters on Mars
- Mars stubs
- Astrogeology stubs
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgPageParseReport":"limitreport":"cputime":"0.376","walltime":"0.490","ppvisitednodes":"value":1256,"limit":1000000,"ppgeneratednodes":"value":0,"limit":1500000,"postexpandincludesize":"value":199180,"limit":2097152,"templateargumentsize":"value":34262,"limit":2097152,"expansiondepth":"value":13,"limit":40,"expensivefunctioncount":"value":0,"limit":500,"unstrip-depth":"value":0,"limit":20,"unstrip-size":"value":5025,"limit":5000000,"entityaccesscount":"value":1,"limit":400,"timingprofile":["100.00% 266.510 1 -total"," 28.11% 74.922 1 Template:Infobox_Mars_crater"," 24.61% 65.580 1 Template:Infobox_crater_data"," 22.89% 61.003 1 Template:Infobox"," 17.54% 46.747 1 Template:Geography_of_Mars"," 16.42% 43.749 1 Template:Navbox_with_collapsible_groups"," 16.38% 43.646 1 Template:Reflist"," 13.33% 35.528 1 Template:About"," 13.08% 34.850 1 Template:Cite_book"," 11.07% 29.514 1 Template:Coord"],"scribunto":"limitreport-timeusage":"value":"0.099","limit":"10.000","limitreport-memusage":"value":4060574,"limit":52428800,"cachereport":"origin":"mw2179","timestamp":"20180917232435","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false);mw.config.set("wgBackendResponseTime":81,"wgHostname":"mw2194"););




 Clash Royale CLAN TAG
Clash Royale CLAN TAG