Lubiprostone
Lubiprostone
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
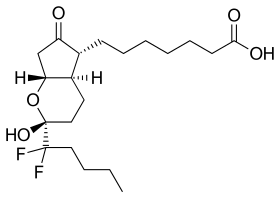
RU-0211
SPI-0211
AHFS/Drugs.com
US FDA: Lubiprostone
category
US: C (Risk not ruled out)
administration
A06AX03 (WHO)
US: ℞-only
Pharmacokinetic data
0.9–1.4 hours (main metabolite)
Renal (60%) and fecal (30%)
- 7-[(1R,3R,6R,7R)-3-(1,1-Difluoropentyl)-3-hydroxy-8-oxo-2-oxabicyclo[4.3.0]non-7-yl]heptanoic acid
136790-76-6 Y
Y
PubChem CID
- 157920
- 4242
DB01046 Y
Y
138948 Y
Y
- 7662KG2R6K
D04790 Y
Y
ChEMBL1201134 N
N
100.107.168
C20H32F2O5
- Interactive image
- FC(F)(CCCC)[C@]2(O)O[C@@H]1CC(=O)[C@@H]([C@H]1CC2)CCCCCCC(=O)O
- InChI=1S/C20H32F2O5/c1-2-3-11-19(21,22)20(26)12-10-15-14(16(23)13-17(15)27-20)8-6-4-5-7-9-18(24)25/h14-15,17,26H,2-13H2,1H3,(H,24,25)/t14-,15-,17-,20-/m1/s1
 Y
Y - Key:WGFOBBZOWHGYQH-MXHNKVEKSA-N
 Y
Y
.mw-parser-output .noboldfont-weight:normal
(verify)
Lubiprostone (rINN, marketed under the trade name Amitiza among others) is a medication used in the management of chronic idiopathic constipation, predominantly irritable bowel syndrome-associated constipation in women and opioid-induced constipation.
It was initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2006 and recommended for use in the UK by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in 2014.[1] It is expensive as of 2017, with the cost to the NHS being £29.68 per 24mg 28-cap pack as of April 2017.[2]
Contents
1 Medical uses
2 Adverse effects
2.1 Contraindications
3 Mechanism of action
4 Pharmacokinetics
5 Society and culture
5.1 Legal status
5.2 Brand names
6 References
7 External links
Medical uses[edit]
Lubiprostone is used for the treatment of chronic constipation of unknown cause in adults, as well as irritable bowel syndrome associated with constipation in women.[3]
Lubiprostone is approved to treat chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) in adults.
Lubiprostone is also approved to treat opioid-induced constipation, in adults with chronic non-cancer pain. The effectiveness of lubiprostone has not been established in patients who are taking a diphenylheptane opioid (e.g., methadone).
Lubiprostone is approved to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) in women 18 years of age and older.
As of 12 November 2014, lubiprostone has not been studied in children. There is current research underway to determine the safety and efficacy in postoperative bowel dysfunction.
Adverse effects[edit]
In clinical trials, the most common adverse event was nausea (31%). Other adverse events (≥5% of patients) included diarrhea (13%), headache (13%), abdominal distention (5%), abdominal pain (5%), flatulence (6%), sinusitis (5%) vomiting (5%) and fecal incontinence (1%).
Contraindications[edit]
There are no current data on use in people with liver or kidney complications. The effects on pregnancy have not been studied in humans but testing in Guinea pigs resulted in fetal loss.
Amitiza is not approved for use in children. Lubiprostone is contraindicated in patients exhibiting chronic diarrhea, bowel obstruction, or diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.
Mechanism of action[edit]
Lubiprostone is a bicyclic fatty acid derived from prostaglandin E1 that acts by specifically activating ClC-2 chloride channels on the apical aspect of gastrointestinal epithelial cells, producing a chloride-rich fluid secretion. These secretions soften the stool, increase motility, and promote spontaneous bowel movements (SBM).
Symptoms of constipation such as pain and bloating are usually improved within one week, and SBM may occur within one day.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Unlike many laxative products, lubiprostone does not show signs of tolerance, dependency, or altered serum electrolyte concentration. There was no rebound effect following withdrawal of treatment, but a gradual return to pre-treatment bowel movement frequency should be expected.
Minimal distribution of the drug occurs beyond the immediate gastrointestinal tissues. Lubiprostone is rapidly metabolized by reduction/oxidation, mediated by carbonyl reductase. There is no metabolic involvement of the hepatic cytochrome P450 system. The measurable metabolite, M3, exists in very low levels in plasma and makes up less than 10% of the total administered dose.
Data indicate that metabolism occurs locally in the stomach and jejunum.
Society and culture[edit]
Legal status[edit]
Lubiprostone received approval from the Food and Drug Administration in 2008 to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) and is available through prescription only. As of 2014[update], the drug is available in the United States, Japan, Switzerland,India and the United Kingdom; review by Health Canada began in late 2014.[4]
Brand names[edit]
In Bangladesh and India, lubiprostone is marketed under the trade name Lubilax by Beacon Pharmaceuticals Limited, and under the trade name Lubowel by SunPharma.
References[edit]
This article includes a list of references, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. (April 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
^ "Lubiprostone for treating chronic idiopathic constipation - Technology appraisal guidance [TA318]". NICE. 23 July 2014. Retrieved 13 April 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
[dead link]
^ "LUBIPROSTONE - Other drugs used in constipation". British National Formulary. 2014. Retrieved 13 April 2017.
[dead link]
^ "Amitiza". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
^ House, Douglas W. (31 December 2014). "Canada accepts Sucampo's NDS for constipation med". Seeking Alpha.
.mw-parser-output .refbeginfont-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ullist-style-type:none;margin-left:0.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>ddmargin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100font-size:100%
Katzung, B.G. (2007). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 10th edition. McGraw-Hill.
"Clinical Pharmacology Online Database". Archived from the original on December 16, 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
External links[edit]
- Official Website
Categories:
- Drugs acting on the gastrointestinal system and metabolism
- Fatty acids
- Laxatives
- Organofluorides
- Alcohols
- Ketones
- Oxygen heterocycles
- Heterocyclic compounds (2 rings)
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgPageParseReport":"limitreport":"cputime":"0.732","walltime":"0.957","ppvisitednodes":"value":6417,"limit":1000000,"ppgeneratednodes":"value":0,"limit":1500000,"postexpandincludesize":"value":199118,"limit":2097152,"templateargumentsize":"value":9485,"limit":2097152,"expansiondepth":"value":16,"limit":40,"expensivefunctioncount":"value":5,"limit":500,"unstrip-depth":"value":1,"limit":20,"unstrip-size":"value":14917,"limit":5000000,"entityaccesscount":"value":1,"limit":400,"timingprofile":["100.00% 746.355 1 -total"," 55.15% 411.645 1 Template:Drugbox"," 40.30% 300.816 1 Template:Infobox"," 16.60% 123.896 6 Template:Navbox"," 16.05% 119.821 1 Template:Reflist"," 12.15% 90.666 16 Template:Unbulleted_list"," 11.09% 82.781 4 Template:Cite_web"," 10.92% 81.495 1 Template:Refimprove"," 7.82% 58.398 1 Template:Prostanoidergics"," 7.06% 52.674 2 Template:Ambox"],"scribunto":"limitreport-timeusage":"value":"0.243","limit":"10.000","limitreport-memusage":"value":5315227,"limit":52428800,"cachereport":"origin":"mw1296","timestamp":"20181227113915","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false););"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"Lubiprostone","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lubiprostone","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q6695342","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q6695342","author":"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects","publisher":"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png","datePublished":"2006-12-25T17:21:02Z","dateModified":"2018-06-23T10:59:03Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/d3/Lubiprostone.svg","headline":"chemical compound"(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function()mw.config.set("wgBackendResponseTime":104,"wgHostname":"mw1332"););

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG
Clash Royale CLAN TAG